07-30-2017, 01:39 AM
I got the following from Wikipedia istribution
istribution
[url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:World_plankton_prevailence.PNG"]![[Image: 400px-World_plankton_prevailence.PNG]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/be/World_plankton_prevailence.PNG/400px-World_plankton_prevailence.PNG) [/url]
[/url]
[url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:World_plankton_prevailence.PNG"][/url]
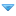
World distribution of plankton
Plankton inhabit oceans, seas, lakes, ponds. Local abundance varies horizontally, vertically and seasonally. The primary cause of this variability is the availability of light. All plankton ecosystems are driven by the input of solar energy (but see [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chemosynthesis"]chemosynthesis[/url]), confining primary production to surface waters, and to geographical regions and seasons having abundant light.
A secondary variable is nutrient availability. Although large areas of the [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tropics"]tropical[/url] and [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sub-tropical"]sub-tropical[/url] oceans have abundant light, they experience relatively low primary production because they offer limited nutrients such as [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nitrate"]nitrate[/url], [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphate"]phosphate[/url] and [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Silicate"]silicate[/url]. This results from large-scale [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ocean_current"]ocean circulation[/url] and water column [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stratification_(water)"]stratification[/url]. In such regions, primary production usually occurs at greater depth, although at a reduced level (because of reduced light).
Despite significant [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Macronutrient"]macronutrient[/url] concentrations, some ocean regions are unproductive (so-called [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HNLC"]HNLC regions[/url]).[url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plankton#cite_note-14"][14][/url] The [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Micronutrient"]micronutrient[/url] [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iron"]iron[/url] is deficient in these regions, and adding it can lead to the formation of phytoplankton [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Algal_bloom"]blooms[/url].[url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plankton#cite_note-15"][15][/url] Iron primarily reaches the ocean through the deposition of dust on the sea surface. Paradoxically, oceanic areas adjacent to unproductive, [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arid"]arid[/url] land thus typically have abundant phytoplankton (e.g., the eastern [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atlantic_Ocean"]Atlantic Ocean[/url], where [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trade_winds"]trade winds[/url] bring dust from the [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sahara_Desert"]Sahara Desert[/url] in north [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Africa"]Africa[/url]).
While plankton are most abundant in surface waters, they live throughout the water column. At depths where no primary production occurs, [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zooplankton"]zooplankton[/url] and [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bacterioplankton"]bacterioplankton[/url] instead consume organic material sinking from more productive surface waters above. This flux of sinking material, so-called [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marine_snow"]marine snow[/url], can be especially high following the termination of [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spring_bloom"]spring blooms[/url].
[signature]
 istribution
istribution[url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:World_plankton_prevailence.PNG"]
![[Image: 400px-World_plankton_prevailence.PNG]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/be/World_plankton_prevailence.PNG/400px-World_plankton_prevailence.PNG) [/url]
[/url] [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:World_plankton_prevailence.PNG"][/url]
World distribution of plankton
Plankton inhabit oceans, seas, lakes, ponds. Local abundance varies horizontally, vertically and seasonally. The primary cause of this variability is the availability of light. All plankton ecosystems are driven by the input of solar energy (but see [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chemosynthesis"]chemosynthesis[/url]), confining primary production to surface waters, and to geographical regions and seasons having abundant light.
A secondary variable is nutrient availability. Although large areas of the [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tropics"]tropical[/url] and [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sub-tropical"]sub-tropical[/url] oceans have abundant light, they experience relatively low primary production because they offer limited nutrients such as [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nitrate"]nitrate[/url], [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphate"]phosphate[/url] and [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Silicate"]silicate[/url]. This results from large-scale [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ocean_current"]ocean circulation[/url] and water column [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stratification_(water)"]stratification[/url]. In such regions, primary production usually occurs at greater depth, although at a reduced level (because of reduced light).
Despite significant [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Macronutrient"]macronutrient[/url] concentrations, some ocean regions are unproductive (so-called [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HNLC"]HNLC regions[/url]).[url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plankton#cite_note-14"][14][/url] The [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Micronutrient"]micronutrient[/url] [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iron"]iron[/url] is deficient in these regions, and adding it can lead to the formation of phytoplankton [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Algal_bloom"]blooms[/url].[url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plankton#cite_note-15"][15][/url] Iron primarily reaches the ocean through the deposition of dust on the sea surface. Paradoxically, oceanic areas adjacent to unproductive, [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arid"]arid[/url] land thus typically have abundant phytoplankton (e.g., the eastern [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atlantic_Ocean"]Atlantic Ocean[/url], where [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trade_winds"]trade winds[/url] bring dust from the [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sahara_Desert"]Sahara Desert[/url] in north [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Africa"]Africa[/url]).
While plankton are most abundant in surface waters, they live throughout the water column. At depths where no primary production occurs, [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zooplankton"]zooplankton[/url] and [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bacterioplankton"]bacterioplankton[/url] instead consume organic material sinking from more productive surface waters above. This flux of sinking material, so-called [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marine_snow"]marine snow[/url], can be especially high following the termination of [url "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spring_bloom"]spring blooms[/url].
[signature]